40 structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Radionuclide cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow studies or so-called radionuclide ventriculography provide a safe physiologic assessment of the functional anatomy of the CSF spaces [31-33].CSF circulates through the ventricular system and subarachnoid space that surrounds both the brain and spinal cord (Figure 51.21).Normally, CSF flows anteriorly in the lateral ventricles through the foramen of ... quizlet.com › 336935319 › quiz-chapter-14-brainQuiz Chapter 14 - Brain Cranial Nerves Flashcards & Practice ... A child riding a bike falls and hits their head. The child was not wearing a helmet. In the emergency room, cerebrospinal fluid taken during a spinal tap reveals blood. The doctors diagnosed the child had torn cerebral veins as they pass to the superior sagittal sinus. What area of the body was the fluid taken? Epidural space Subarachnoid space
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Lymphatic_systemLymphatic system - Wikipedia The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word lympha refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open.
Structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid
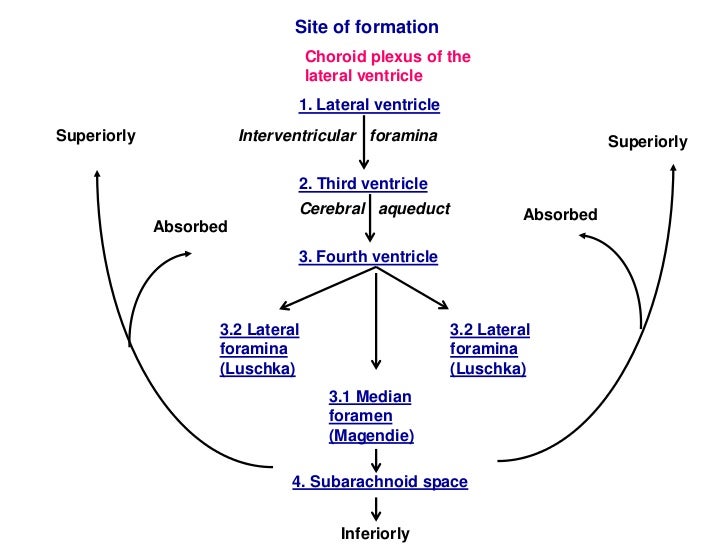
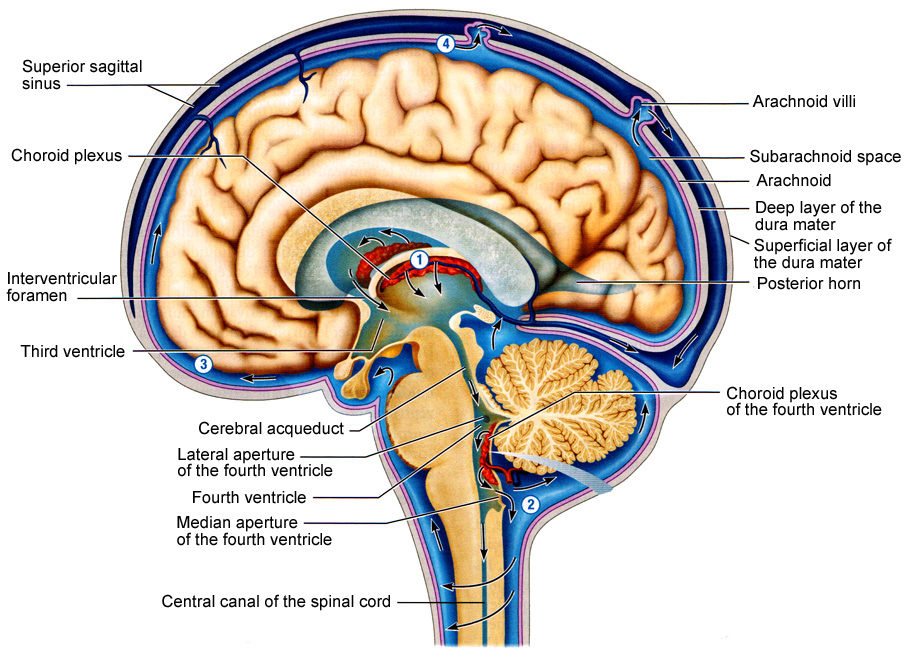
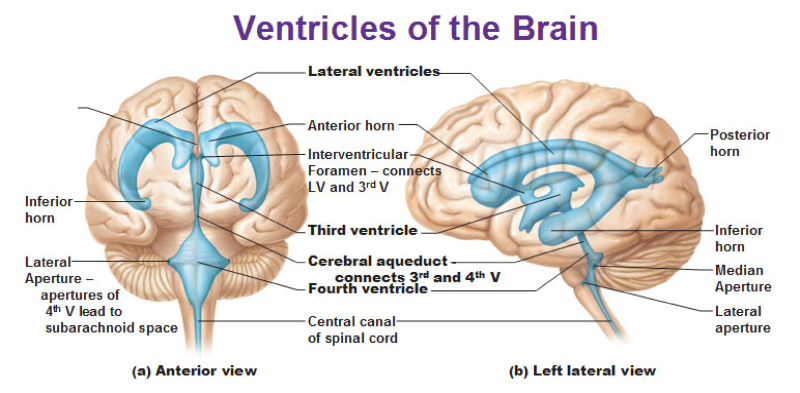
Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Relevant to Hydrocephalus There are four ventricles in all: two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The ventricles are connected by narrow passageways. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) flows through the four ventricles and then flows between the meninges in an area called the subarachnoid space. Solved Cerebrospinal Fluid 10. Label the structures involved | Chegg.com Expert Answer 100% (11 ratings) 1. Lateral ventricle Largest ventricels of the brain locates one in each cerebral hemisphere 2. Thrid ventricle Funnel shaped ,placed in the midline It present between two thalami. 3. Cerebral aquedut Cerebral a … View the full answer Transcribed image text: Cerebrospinal Fluid 10. › Media › Glossary-of-TerminologyGlossary and Definitions of Neurosurgical Terminology No radiation is involved, but rather pulsed magnetic waves used to delineate the structures within the brain. MYELIN - The fat-like substance that surrounds the axon of nerve fibers and forms an insulating material. MYELOGRAM - An x-ray of the spinal canal following injection of a contrast material into the surrounding cerebrospinal fluid spaces.
Structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Cerebral circulation & csf formation - SlideShare CSF ( Cerebrospinal fluid physiology) circulation upendra bhardwaj. Y2 s1 csf vajira54. Csf formation, absorption and circulation Dr Sara Sadiq. Csf circulation and low csf pressure headaches ... (midline view) showing the anatomical structures involved in the production and flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricular system, brain and ... Structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid? - Answers Structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid? Wiki User. ∙ 2010-12-15 05:27:46. Add an answer. ... Structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid? PDF The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system - IAHE The functional anatomy of the structures responsible for the return of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the general cir- culation is based on somewhat conflicting evidence as to their location, anatomical features, and functional capa- bilities. › pmc › articlesNeuropharmacology of N,N-Dimethyltryptamine - PMC 2.5. Detection of endogenous DMT in blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid. DMT as an endogenous compound can be measured in human body fluids, including blood, urine and cerebral spinal fluid. Levels of endogenous DMT do not appear to be regulated by diet or gut bacteria (Barker et al., 2012). Infrequent and inadequate sampling methods used ...
Blood Vessels and Cerebrospinal Fluid - TeachMeAnatomy In this article in our blood vessels and CSF section, we shall look at the arterial structures supplying the brain and spinal cord. The venous drainage of the central nervous system is complex, and rather uniquely, does not follow the arterial supply. The cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem are drained by numerous veins, which empty into the ... The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system This review traces the development of our understanding of the anatomy and physiological properties of the two systems responsible for the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the systemic circulation. The roles of the cranial and spinal arachnoid villi (AV) and the lymphatic outflow systems … › en › libraryCerebrospinal fluid flow: Anatomy and functions | Kenhub Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through a system of cavities found within the brain and spinal cord; ventricles, subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord and the central canal of the spinal cord. Most CSF is secreted by the specialized tissue called the choroid plexus, which is located within the lateral, third and fourth ventricles. The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system Abstract. This review traces the development of our understanding of the anatomy and physiological properties of the two systems responsible for the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the systemic circulation. The roles of the cranial and spinal arachnoid villi (AV) and the lymphatic outflow systems are evaluated as to the dominance of ...
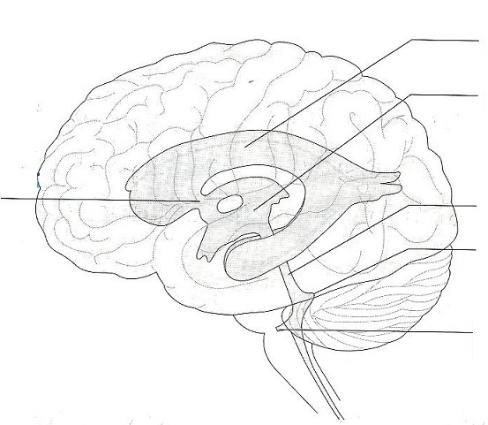
Solved 10. Label the structures involved with circulation of - Chegg Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram Add arrows to the figure above to indicate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from its formation in the lateral ventricles to the site of its exit from the fourth ventricle. Then fill in the blanks in the following paragraph. The circulation and function of cerebrospinal fluid - PubMed The distribution of corpora and the action of intrathecal vincristine suggested that CSF is recirculated through the ventricular system. A complete cycle of ventricular fluid could set the pace of the 100 minute ultradian rhythm found in human beings. Arachnoid granulations were not in an area of high volume of flow of the fluid and probably do ... Cerebrospinal Fluid - Flow of CSF - TeachMePhysiology The CSF is produced by the choroid plexus which covers two lateral ventricles, and the roof of the third and fourth ventricles. Around 500 ml of CSF is produced each day, with around 150 ml being present in the body at any given time. The choroid plexus is composed of fenestrated capillary loops, covered by a layer of specialised ependymal cells. Cerebrospinal fluid - Wikipedia Cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations.
Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) - IntechOpen 2. Physiology of circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The CSF physiology, in the classical sense, is based mainly on animal experiments . In recent research, the structure of CSF circulation has been questioned, challenging significant aspects of the classical model. Recently, CSF production and absorption have been reevaluated [9, 29, 30, 31].
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Composition, Circulation and Function Most of CSF gets absorbed into arachnoid villi and granulations which dip into subdural venous sinuses. Subarachnoid spaces can be reached either by lumbar or cisternal puncture. Lumbar puncture is preferred because cisternal puncture requires insertion of needle into subarachnoid spaces near brainstem region.
A new look at cerebrospinal fluid circulation - PMC The traditional understanding of CSF physiology assumes that 80% of CSF is secreted by the choroid plexus into the ventricular cavities. Other structures, e.g. the brain parenchyma, add the remaining 20%. The rate of CSF formation in humans is 0.3 - 0.4 ml min -1, and the total CSF volume is 90 - 150 ml in adults.
14.2 Blood Flow the meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid Production and ... Venous Return. After passing through the CNS, blood returns to the circulation through a series of dural sinuses and veins (Figure 14.2.2).The superior sagittal sinus runs in the groove of the longitudinal fissure, where it absorbs CSF from the meninges. The superior sagittal sinus drains to the confluence of sinuses, along with the occipital sinuses and straight sinus, to then drain into the ...
Cerebrospinal fluid, its formation and circulation - The Science Info The total volume of CSF i.e. about 125ml in adult is formed and renewed about three times a day. Circulation of CSF. CSF moves from the ventricles inside the brain to the subarachnoid space outside the brain normally. It flows slowly from the two lateral ventricles of the brain, where much of the fluid is formed.
Solved > 14.Label the structures involved with circulation of ... 14.Label the structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid on the accompanying diagram. Add arrows to the figure above to indicate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from its formation in the lateral ventricles to the site of its exit from the fourth ventricle. Then fill in the blanks in the following paragraph. Solution 5 (1 Ratings )
› pmc › articlesThe Glymphatic System – A Beginner's Guide - PMC The fluid compartments in the brain consist of intracellular fluid (ICF) (60-68%), interstitial fluid (ISF) (or extracellular fluid) (12-20%), blood (10%) and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (10%) [5, 10]. The blood is separated from the CSF and interstitial fluid by the blood brain barrier (BBB) and blood-CSF barrier, respectively.
Flow of Cerebrospinal Fluid Flashcards - Quizlet CSF flows out two lateral apertures and one medial aperture. What happens at stage 6? CSF fills subarachnoid space and bathes external surfaces of brain and spinal cord. What happens at stage 7? At arachnoid villi, CSF if reabsorbed into venous blood of dural venous sinuses. What happens at stage 8? Recommended textbook explanations


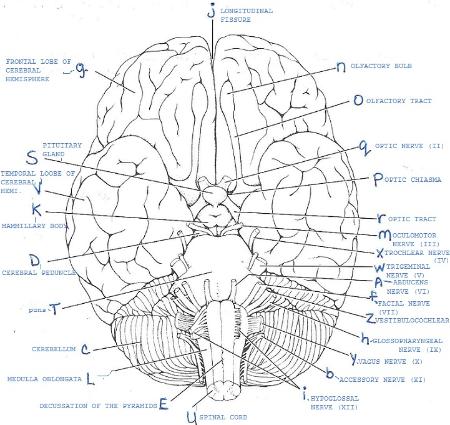
Post a Comment for "40 structures involved with circulation of cerebrospinal fluid"